records
Delay and frustration in adoption law’s first year
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/articles/cp3dx01v8x8o
Delay and frustration in adoption law’s first year

At a glance
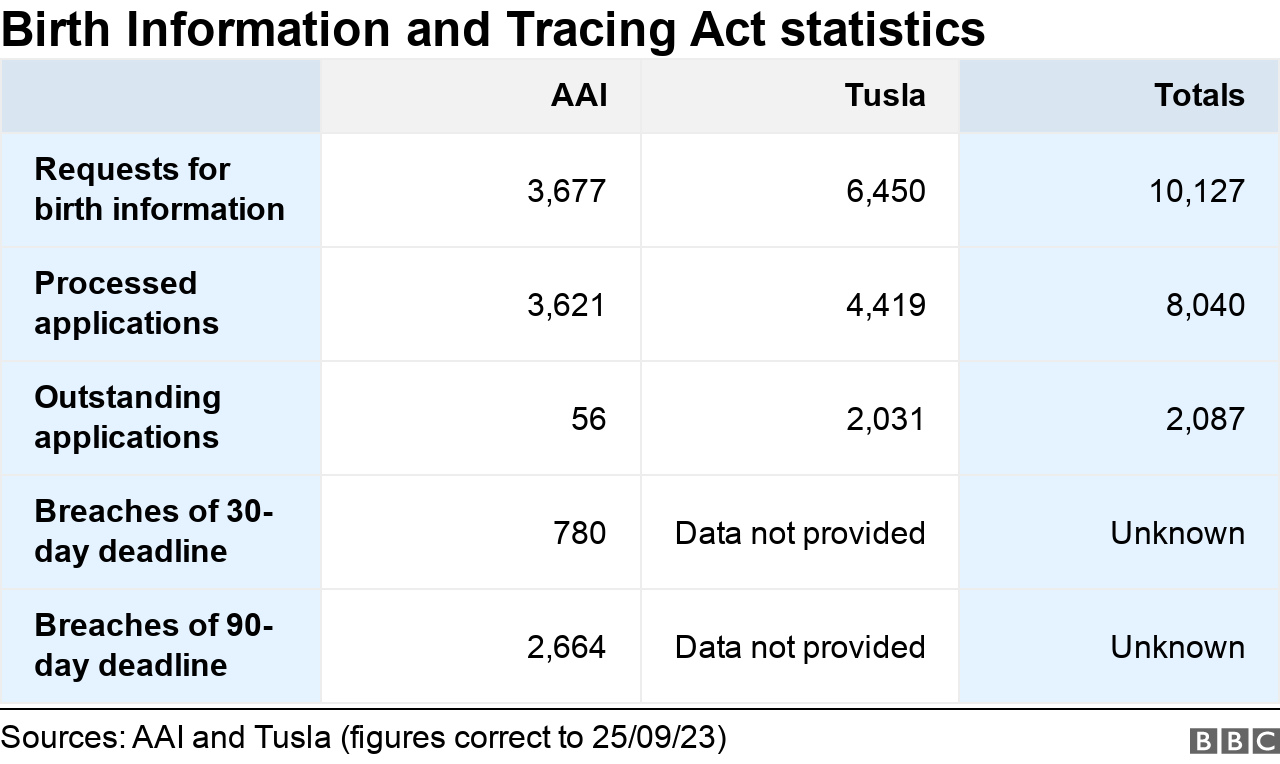
- More than 10,000 requests for adoptees’ birth records have been submitted during the first year of a new Irish law
- The authorities struggled to meet demand and missed legal deadlines
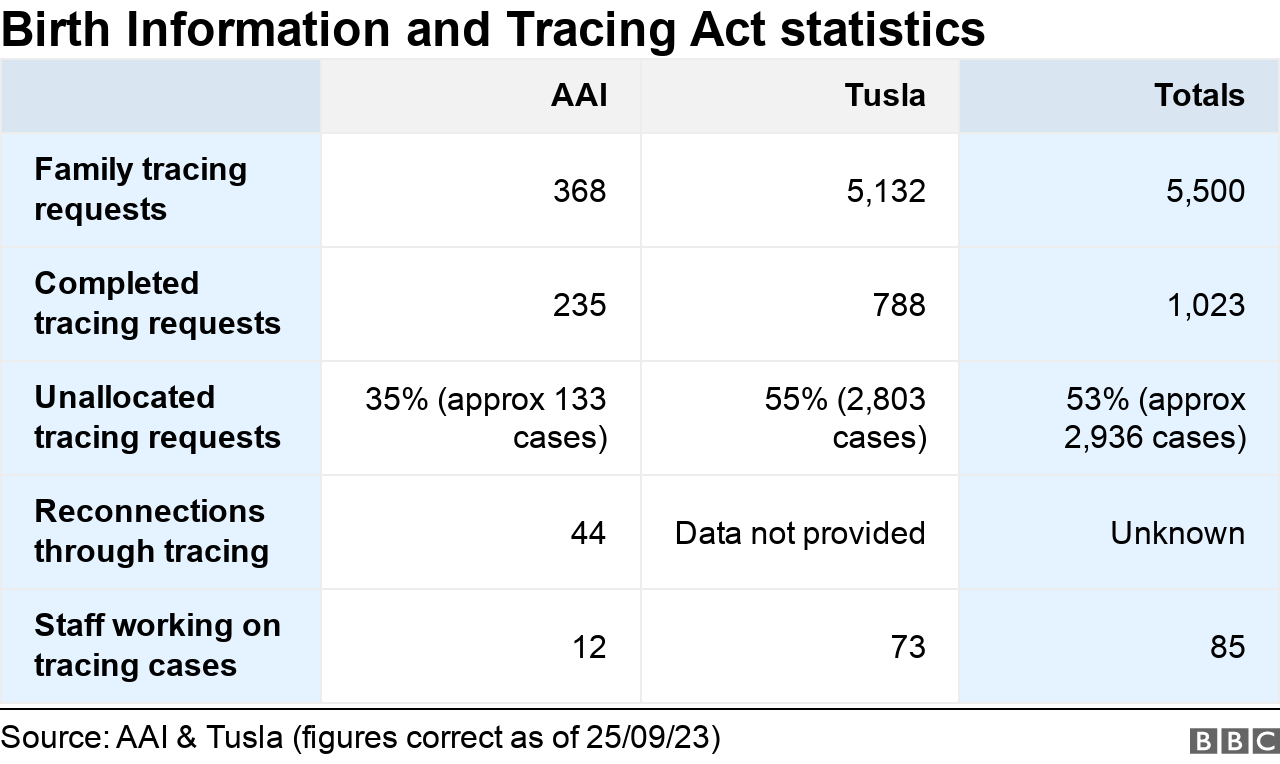
- A total of 5,500 requests were made to use a new family tracing service
- More than half (53%) of tracing requests are yet to be allocated to staff
Eimear Flanagan
BBC News NI
- Published3 October 2023
An Irish law that gave adopted people the right to access their birth records has led to more than 10,000 applications during its first year of operation.
The Birth Information and Tracing Act, external was designed to end much of the secrecy embedded in Ireland’s 70-year-old adoption system.
But for many adoptees waiting decades for answers about their early lives, the new procedures meant delays and frustration.
The legislation created a new family tracing service and throughout the year 5,500 requests to find relatives were submitted.
However, due to the complexity of some searches, 53% of tracing requests are yet to be allocated to staff.
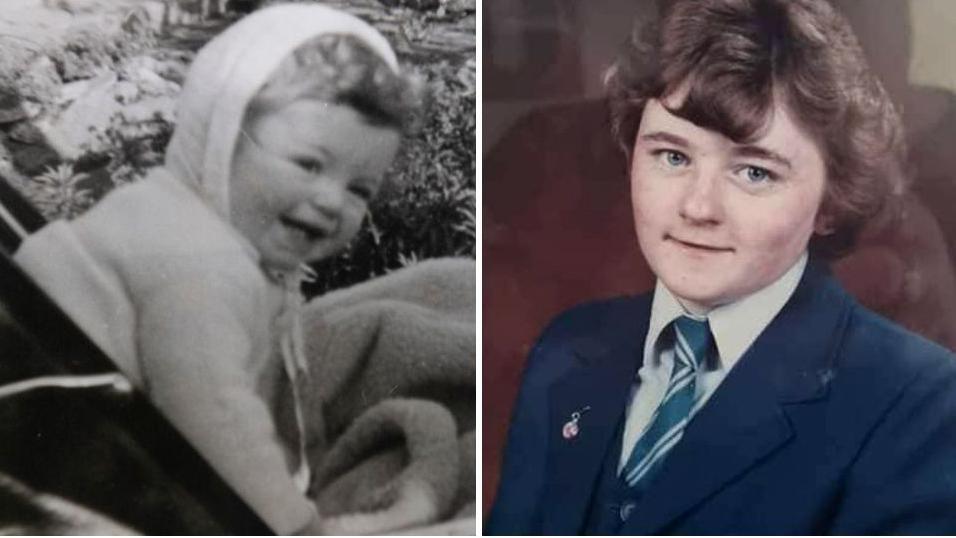
“I am relying on a system that is working at a snail’s pace,” said Linda Southern, who is searching for her birth parents.
The 48-year-old Dubliner was adopted in 1975 at six weeks of age.
She spent her first 47 years not knowing her birth name nor the names of her mother and father.

That is because until 3 October 2022, Irish adoptees had no automatic right to see their own birth certificates, nor to know their biological parents’ identities.
The new law was supposed to give adoptees access to birth records within 30 days, or 90 days in complex cases.
Two organisations tasked with releasing records struggled to handle an early surge of applications.
The Adoption Authority of Ireland (AAI) and child and family agency Tusla both missed statutory deadlines.
“The initial surge led to wait times which would be frustrating and which we regret,” said AAI interim chief executive Colm O’Leary.
“When you’re starting off a process and you’re learning that records are held across various sources, it takes time to become familiar with all of the record types,” he explained.
A Tusla spokeswoman said “a significant portion of the applications are classified as complex which means they require more time”.
But adoptees argue authorities should have been better prepared.

“Surely, state bodies would have had a basic idea of the number of adoptees who would want to at least get their birth information,” said Ms Southern.
After initial delays, she received her own documents which – for the first time – revealed her original name and parents’ names.
However, she still needs help finding her biological family and spent the past year waiting for news.
“I don’t know if they will ever trace my birth mother or not.
“If they can’t, I should be told,” she said.
“They should have presumed the majority would want to trace – better to presume that too many people would wish to trace birth families than too few.”
‘Belfast baby’
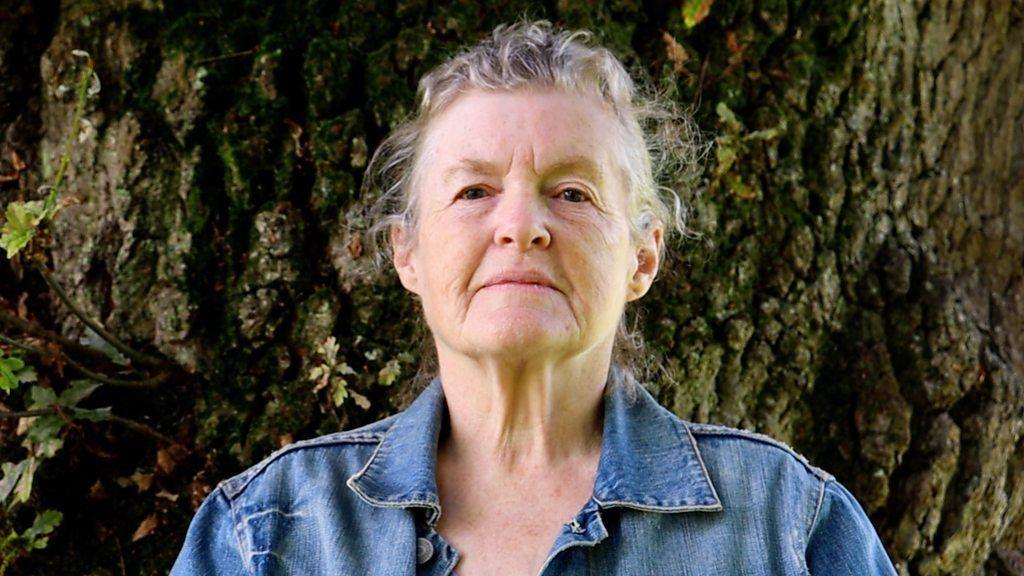

Loraine Jackson had hoped her birth files might shed some light on her cross-border adoption.
She grew up in Dublin, with barely any information about her birth.
But in her early 40s, she found out she was actually a native of the United Kingdom, having been born to a single mother in Belfast in 1948.
Her parents died years before she could trace them.
When she spoke to BBC News NI last year, she expressed hope her files might reveal how or why she was taken across the border for adoption.
After months of waiting, a “fat package” arrived in the post which included an unredacted version of her adoption agreement.
For the first time, she saw her relatives’ signatures and finally found out who authorised her adoption.

“My birth mother had not been present at the signing. Her sister signed for her,” Ms Jackson explained.
She also expected her files would contain information about the standard of care she received in Bethany children’s home in Dublin.
But apart from a photocopy of her name in Bethany’s admission book, she was disappointed.
“The information just didn’t seem to be there. Whether records were not kept as well in those days, I don’t know.”
Although left with many unanswered questions, her maternal aunt’s role in her adoption was new information to her.
“It was definitely worthwhile doing, and I’d advise anyone who hasn’t applied yet to go for it.”
AAI staff received a wide range of feedback from adoptees about their birth files – from delight to disappointment to disbelief.
“A lot of people have said: ‘Is that it? Is there nothing else?'” Mr O’Leary said.
He acknowledged some adoptees were dismayed to learn that nothing more exists on file than details they already knew.
Others have received heavily censored documents.
“Sometimes the authority gets records that are already redacted prior to us getting them… we cannot unredact it,” Mr O’Leary explained.
He also said AAI staff can apply redactions themselves, in cases where personal information refers to a third party.
However, he added applicants can request a review if they believe files were “inappropriately redacted”.

The interim chief executive acknowledged the AAI’s 12 social workers have “significant” tracing workloads.
But he said tracing “is not a linear process” and adoptees often pause the search themselves to digest new information.
“You’re dealing with a very emotive situation,” Mr O’Leary said.
“People may initiate a trace, thinking that their birth mother would want to hear from them, and they have to take on board that the birth mother does not want contact.”
But the new law produced positive outcomes too – the AAI’s tracing service has facilitated 44 family reunions.
“Sometimes I’ll go to the kitchen and I’ll see a social worker taking out the fancy crockery and making tea” Mr O’Leary said.
“They’re bringing it into a room where a family is being reunited.”
He added that when staff help connect families “there is a sense of success, and of delivering on the legislation”.

The AAI’s backlog of birth record applications is almost cleared and by last week, just 56 were outstanding.
Tusla has a much larger backlog which it expects to clear by June 2024.
It said from1 September, all new applications are being processed “within statutory timelines”.
If you are affected by the issues raised in this story, help and support can be found at BBC Action Line.