admin
Reflection of adoption
It’s coming up for the most hated time of the year for me. It will be 44 years on the 3rd August that my son was born and it doesn’t get any easier. I shouldn’t let it get to me so much yet it still does and I still can’t talk about it either. It probably comes down to I was expected to carry on as normal as if nothing had happened.
I can still remember my son being born as is it was a recent event. There wasn’t anybody to celebrate with and my tears were of pain and sadness not happiness. I insisted on seeing him and that was the only time I felt happy knowing how beautiful he was. At the same time I knew deep down that this was one battle I wouldn’t win and I wouldn’t raise him.
Reflection on adoption
I haven’t spent time writing anything on adoption and me as it seemed easier not think about it. Even when conversations have come round to children I tend to deflect or keep quiet. My friends I.R.L don’t have an adoption connection so it can be hard to mention anything particularly as my son and I don’t talk. One friend’s daughter has been approved to adopt and I know I can talk with this friend as she knows the basics. I’d rather be able to talk to someone even as an adoptive grandmother as it may help knowing that cut backs are happening with adoption support. It’s wrong as the children need as much support as possible.
To be continued …..
I was branded Britain’s most hated woman for buying twin babies online for £8k in ‘cash for babies scandal’… here’s what happened next
https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-14831519/Britain-hated-woman-buying-twin-babies.html
I was branded Britain’s most hated woman for buying twin babies online for £8k in ‘cash for babies scandal’… here’s what happened next
- Do YOU have a story? Email tips@dailymail.com
Published: 16:04, 22 June 2025 | Updated: 17:08, 22 June 2025
She was branded the most hated woman in Britain after paying more than £8,000 to buy twin babies from the US on the internet.
Judith Kilshaw found herself at the centre of an international scandal after adopting the six-month old girls who had already been sold to a childless couple in America.
More than 20 years on, Judith admits her life had been ‘plagued’ by the global controversy which ended with her losing the children – along with her home and her marriage.
But defiant Judith, 71, insists she has ‘no regrets’ and told how she has not given up hope of being reunited with the twins.
Speaking exclusively to MailOnline from her home in Wrexham, Judith told MailOnline: ‘I have thought a lot about the case over the years and asked myself if I regretted doing it.
‘To a certain extent it has plagued my life – it never goes away.
‘It was a nightmare to start with but time heals things. There’s bigger things to think about.
‘But I have no regrets. I thought I could give the girls a better life and give them opportunities in life.

Judith Kilshaw (pictured) found herself at the centre of an international scandal after adopting the six-month old girls who had already been sold to a childless couple in America

Alan and Judith Kelshaw (pictured) sparked a ‘cash-for babies’ outcry in 2001 after they paid £8,200 to adopt Kiara and Keyara Wecker

Two six month old twin girls, Kimberley (right) and Belinda (left) sit on a sofa in Chester in Jan 2001

The front page of the Daily Mail in January 2001 which features the story

Judith (pictured) settled back into relative obscurity but much has happened in the intervening years, which can be revealed for the first time by MailOnline
‘I am open to speaking to them but I have never spoken to them. But if they wanted to, I would love to get in touch.’
Judith and her solicitor husband Alan sparked a ‘cash-for babies’ outcry in 2001 after they paid £8,200 to adopt Kiara and Keyara Wecker.
They brought the twins, who they renamed Belinda and Kimberley, to Britain hoping to start a new life as a family at their seven-bedroom farmhouse in Buckley, north Wales.
But things did not go according to plan.
Then-prime minister Tony Blair called the adoption deal ‘disgusting’ and the twins were seized by social services and taken into emergency protection.
They were returned to the US after a High Court judge annulled the adoption.
Since then, Judith settled back into relative obscurity but much has happened in the intervening years, which can be revealed for the first time by MailOnline.
In the aftermath of the scandal, things were never quite the same for the couple and, saddled with debts over the affair, they were evicted from their farmhouse months later.
They moved into a bungalow in Chester but their 14-year marriage ended after Judith met a man 13 years her junior in a nightclub.
Despite the split, she remained close to Alan and was at his bedside when he died aged 63 in January 2019.
At the time she told of her sadness that he had never fulfilled his dream of meeting the girls again.
She said: ‘He told me he had always regarded the twins as ours and his last wish was for me to go to America and try to make contact with them.
‘I don’t know if this will be possible but I will do everything I can to honour his dying request.’
Before the baby storm erupted, the couple had lived an anonymous, if somewhat eccentric, middle-class life in rural north Wales.
They already had two sons and Judith had two grown up children from her first marriage.

Alan and Judith Kilshaw are pictured with the twin babies

The couple brought the twins, who they renamed Belinda and Kimberley, to Britain hoping to start a new life as a family at their seven-bedroom farmhouse in Buckley, north Wales

Pictured: American couple Richard, 49, and Vickie Allen (right) from California

TV Grab from GMTV showing American couple Richard, 49, and Vickie Allen (right) from California, America, and Britons Alan, 45, and Judith Kilshaw, 47, from Buckley, north Wales (left) who are in dispute over the adoption of babies named Kimberley and Belinda by the Kilshaws

The twins who have now grown up are pictured in a social media post
The couple wanted to have a daughter together but Judith was too old to conceive.
They had spent £4,000 on unsuccessful IVF treatment and had looked into surrogacy before they turned to an online adoption agency in desperation.
The US-based agency called A Caring Heart was run by Tina Johnson who was acting on behalf of the mother of the mixed race twins, Tranda Wecker, who was aged 28 at the time.
Tranda, a hotel receptionist from Missouri, had fallen pregnant as her second marriage was coming to an end and had decided to part with her children.
Unbeknown to Judith and Alan, the broker had already arranged the adoption of the twins with Californian couple Richard and Vickie Allen.
They had paid £4,000 for the adoption and had cared for them for two months.
Tranda reportedly had a change of heart and, while the couple were in the process of finalising legal paperwork, she was given permission to say a final farewell to her daughters.
The American couple were told that Tranda wanted to spend two days with the twins – but instead they were handed to Judith and Alan.

Judith Kilshaw is seen on This Morning in February 2019
They set off with the twins to get their birth certificates before making a gruelling 1,500-mile car journey to Little Rock Arkansas, where adoption is relatively easy, with the Allens in hot pursuit.
After a five-minute hearing the couple return to Britain with the twins and their adoption papers.
But the FBI were called in to probe the case amid a bitter transatlantic war of words and a legal battle over the girls’ future.
The children were returned to the US in April 2001 where they were placed in foster care before a third set of parents eventually raised them.
Judith has always insisted she did nothing wrong or illegal and believed the adoption would be in the best interests of the twins.
But, in the aftermath of the affair, the couple racked up debts of £70,000.
They were forced to quit the farmhouse where they lived with three of Judith’s children along with six dogs, more than a dozen cats, two ferrets, a horse, a pony and two pot-bellied pigs.
In the wake of her fight, Judith tried to get elected as an MP in 2005 after standing as an independent candidate in her local Alyn and Deeside constituency insisting she wanted to ‘stand up for the little people’.
She split with Alan in 2006 and three years later she married Stephen Sillett, who was described at the time as a busker.
In the aftermath of the split, Judith was investigated for alleged benefits fraud arising from her living arrangements following the break-up.
In a bizarre twist, Alan gave his ex-wife away when she married Stephen at Wrexham Register Office in 2009.
She had a volatile relationship with her third husband and in 2012, Judith pleaded guilty at Wrexham Magistrates Court to assaulting Stephen after hitting over the head with a Christmas bauble following a row.
Stephen had accused Judith, who now goes by her married name Sillett, of having an affair, she says.
Judith told MailOnline: ‘It was hardly crime of the century. He probably deserved it.
‘However we stayed together. We are still legally married but have split up.
‘We’re still friends and speak all the time.’
Meanwhile Alan had been struck down with pulmonary fibrosis, a serious lung disease, which left him in hospital for months before his death.
Judith told how Stephen became jealous as she nursed her ex husband through his illness which led to her giving up her job as a cleaner in the Co-op.
She told MailOnline: ‘There were three of us in the relationship and men can’t really handle that can they?
‘I think he didn’t like the attention I was giving Alan.’
Of her life now she added: ‘I now live with my son. I don’t work as I have retired but I’m a bit of an agony aunt to all my friends.’
Speaking from his terraced home in a village near Wrexham, Stephen, now 58, said: ‘We’re still legally married but are not together anymore.
‘I don’t think we can afford to get divorced.’
Judith heard nothing more about the fate of the twins until 2018 when it was revealed they were starting university after being brought up by a loving churchgoing family in Missouri.

Alan, and Judith Kilshaw with Judith’s second husband Stephen Sillett right

Alan and Judith Kilshaw arrive at the High Court in London Monday April 9, 2001

Judith is seen on ITV’s This Morning
Their adoptive mother said at the time: ‘They have grown into fine young women, each with their own dreams and ambitions.’
Since then two TV documentaries have been made about the case – one called Three Mothers, two Babies and a Scandal, which was shown on Amazon Prime in 2022 while a second named The Baby Scandal That Shocked The World was screened on Channel 5 last year.
Judith told MailOnline: ‘The case and furore of it all, never really goes away.
‘In fact I was recognised by a woman in the supermarket the other day.
‘She kept on staring at me, trying to work out who I was. Then she spoke to me asking if I was the woman from the babies case.
‘She recognised me from being on telly a few years ago, but it was positive. She said I came across really well.’
Plaque to be ‘reminder of the pain of forced adoption’
Plaque to be ‘reminder of the pain of forced adoption’

Alex Green
BBC News, South West
Tamsin Melville
BBC Spotlight
- Published10 May 2025
Victims of forced adoption have gathered in Cornwall for a public event condemning the treatment of unmarried mothers in post-war Britain.
They unveiled a plaque at Rosemundy House in St Agnes – formerly a home for unmarried mothers – while calling for a formal “adoption apology” from the government.
Dr Phil Frampton, who was born at the Rosemundy Mother and Baby Home in 1953, said: “We want an apology, not only for the mothers but also for their children who suffered.”
Lyn Rodden, from Camborne, who was one of those forced to give up her baby, said: “It means everything that we’ve been recognised at last.”
‘Struggle for an apology’
It is estimated up to 250,000 women in Britain were forced to give up their babies in the decades after World War Two.
Campaigners also want “restorative actions” from the government, such as providing counselling and search support for mothers and those forcibly adopted.
Dr Frampton, a member of the Rosemundy Commemoration Committee, said he spent years in foster care after he was separated from his mother as a baby.
He said: “It’s really pleasing to be here today, it’s the start of a new chapter in the struggle for an apology for all those unmarried mothers who suffered in the post-war period.”
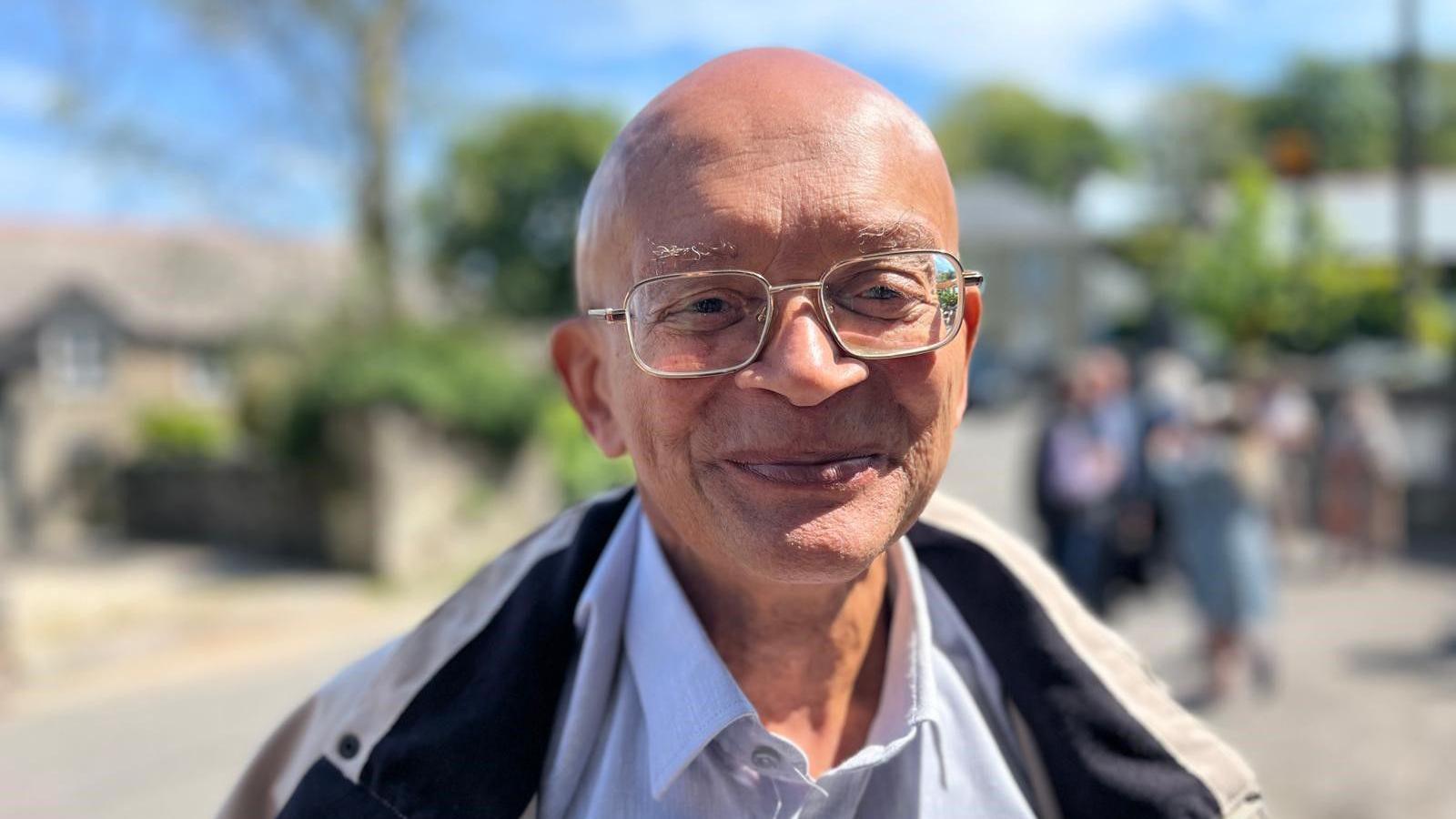

Mr Frampton said the day was “part of a day of healing, part of a day of recognising the grief of those mothers…”
He added: “This is not something that’s just in the past, for a lot of women they lived with this, you hear women today 80, 88 years old, who are still having to live with what happened, and the children live with it, and families live with it.”
Mr Frampton said it was “important” to be able to give the mothers, children, and families affected by forced adoptions “a sense of relief and release”.
Another plaque is due to be unveiled by the campaigners in Kendal, Cumbria, on 23 May.
‘Cried all the way home’
In September 1956, 19-year-old Lyn Rodden from Camborne, Cornwall, gave birth to her son at the Rosemundy home.
She said she was forced to get on a train and take her son to Bath to be adopted.
Ms Rodden said: “For everybody else the parents came here and took them away from here, but I had to get on a train and take my son up to Bath, and leave him in an office.
“A woman just came out and said ‘name’ and ‘I’ll take the baby’ and she took him into the back office, came out and said ‘hurry up’ she said, ‘catch your train’ she said, ‘and back to St Agnes, you’ll be there for another six weeks’.
“That was it. I cried all the way home…”
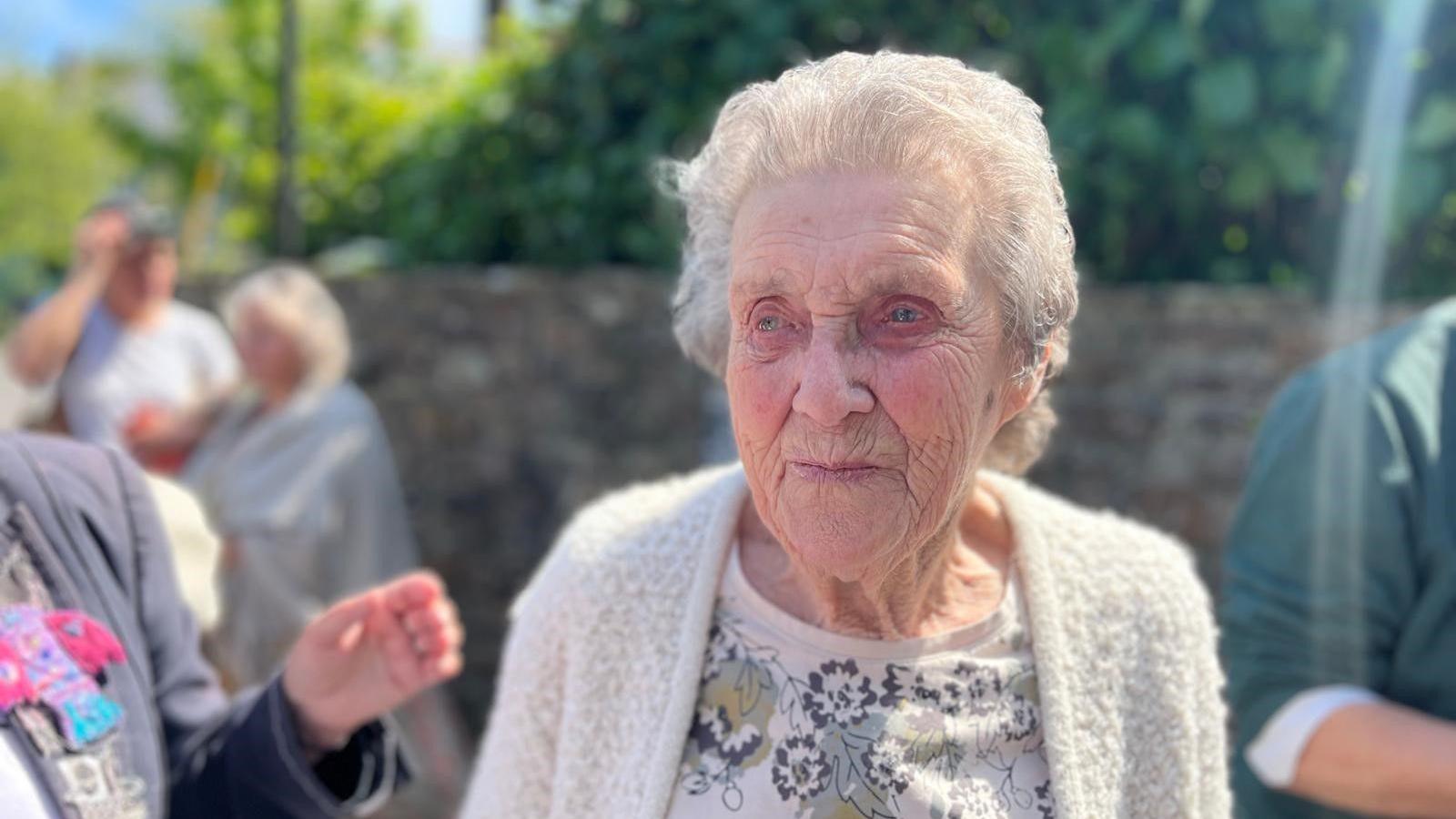

Ms Rodden said she was eventually reunited with her son 50 years later when he found her.
“[It was] like the final piece of a jigsaw being fitted,” she said.
She added: “To think that although slavery was abolished in the 1800s, a Dickensian way of life was gone, but not at Rosemundy.
“It was still in the past, and that was it really, and it means everything that we’ve been recognised at last…”
A Government spokesperson said: “This abhorrent practice should never have taken place, and our deepest sympathies are with all those affected.
“We take this issue extremely seriously and continue to engage with those impacted to provide support.”
The American musician reclaiming his lost Welsh roots
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/articles/c98ggvrqmjdo
The American musician reclaiming his lost Welsh roots

Nicola Bryan
BBC News
- Published20 April 2025
Updated 21 April 2025
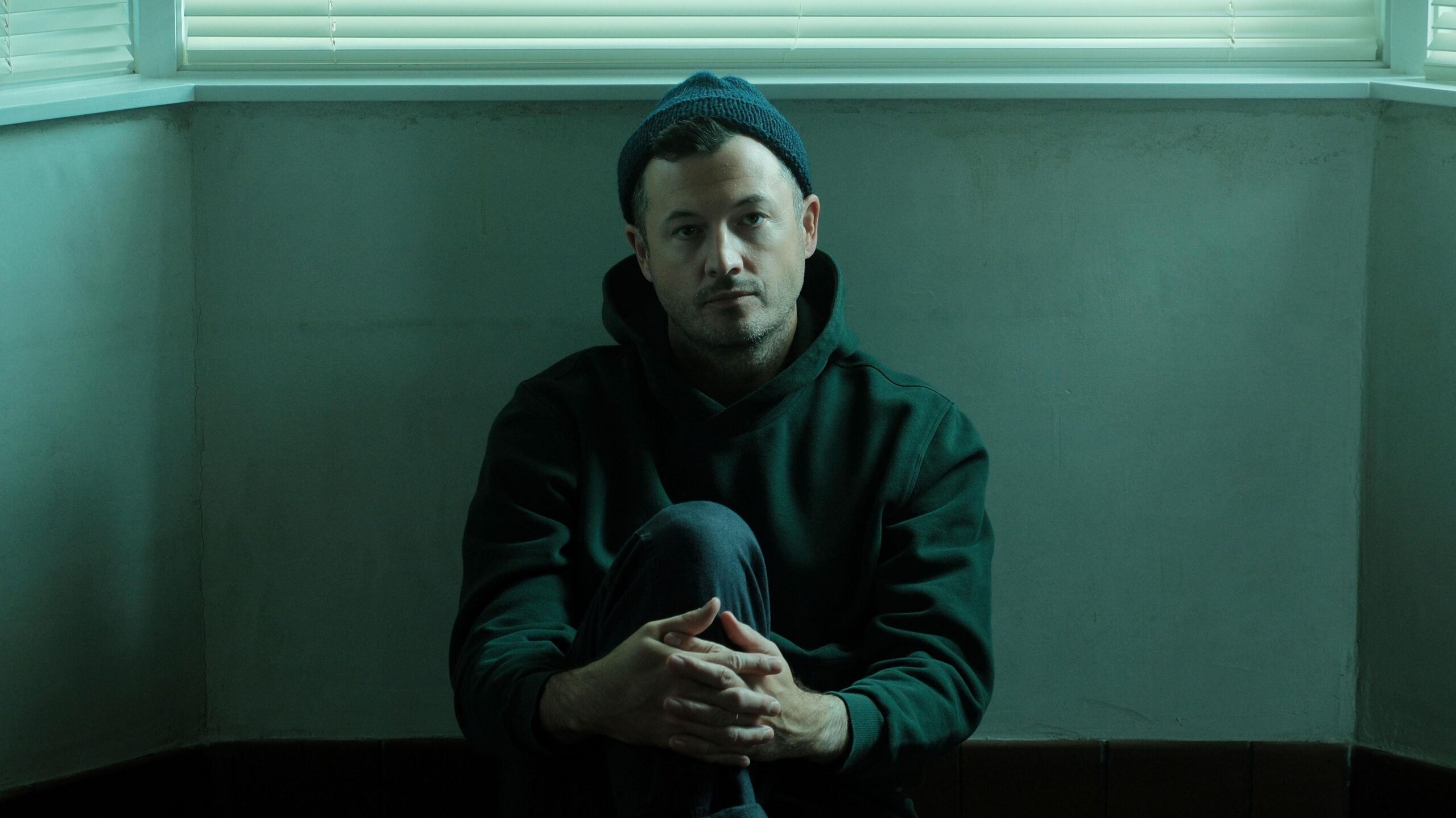
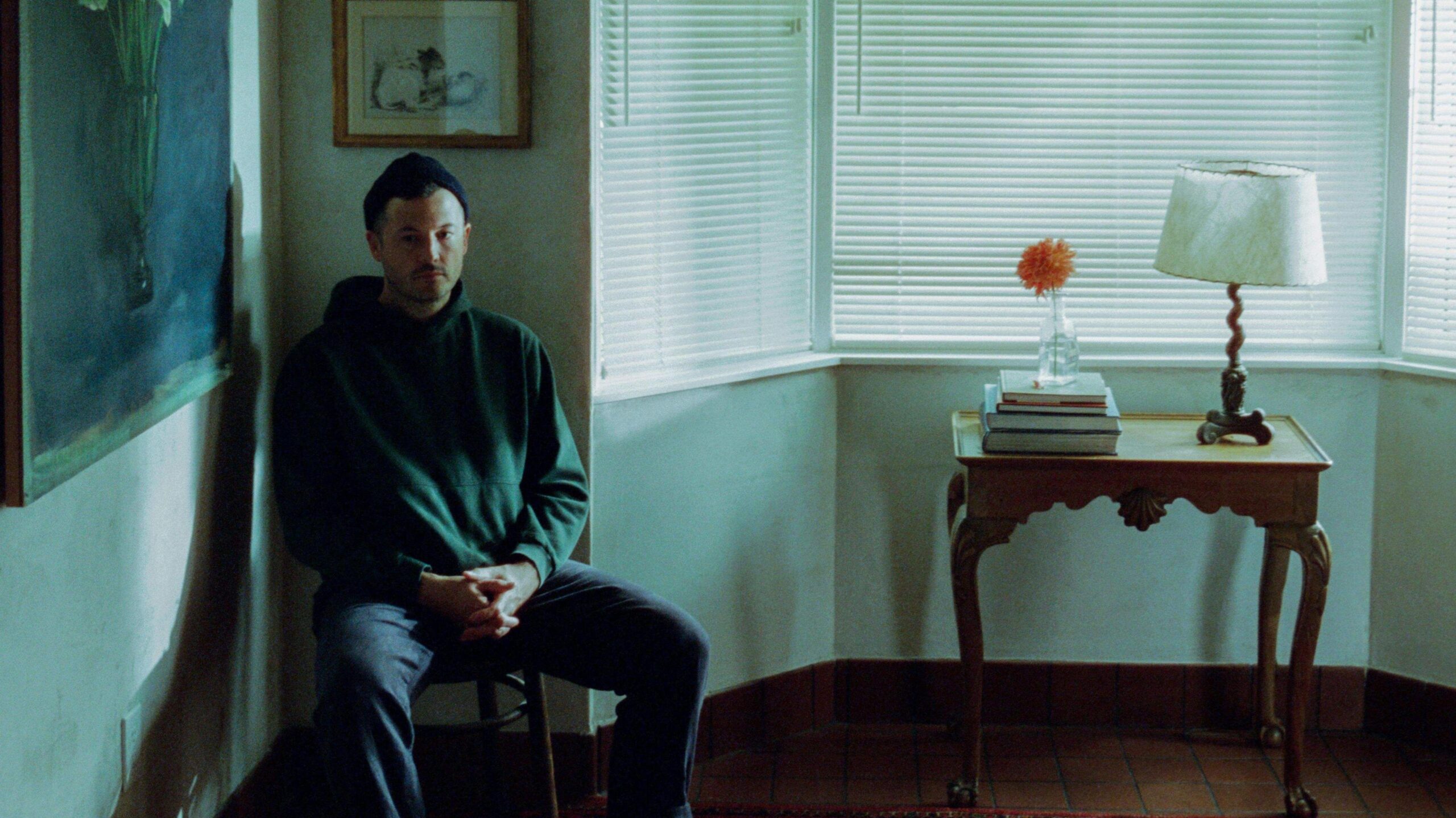
He doesn’t speak Welsh and has only visited the country once but American singer-songwriter Brian Fennell has just released his third studio album using his Welsh alias.
Fennell performs under the name SYML, which means “simple” in Welsh.
Growing up in Seattle he always knew he was adopted, but it was not until he was given his adoption records at 18 that he learnt his birth parents were Welsh.
He said his artist name was a way of honouring his heritage.
“It’s saying that this is where I come from on some level,” he explained.
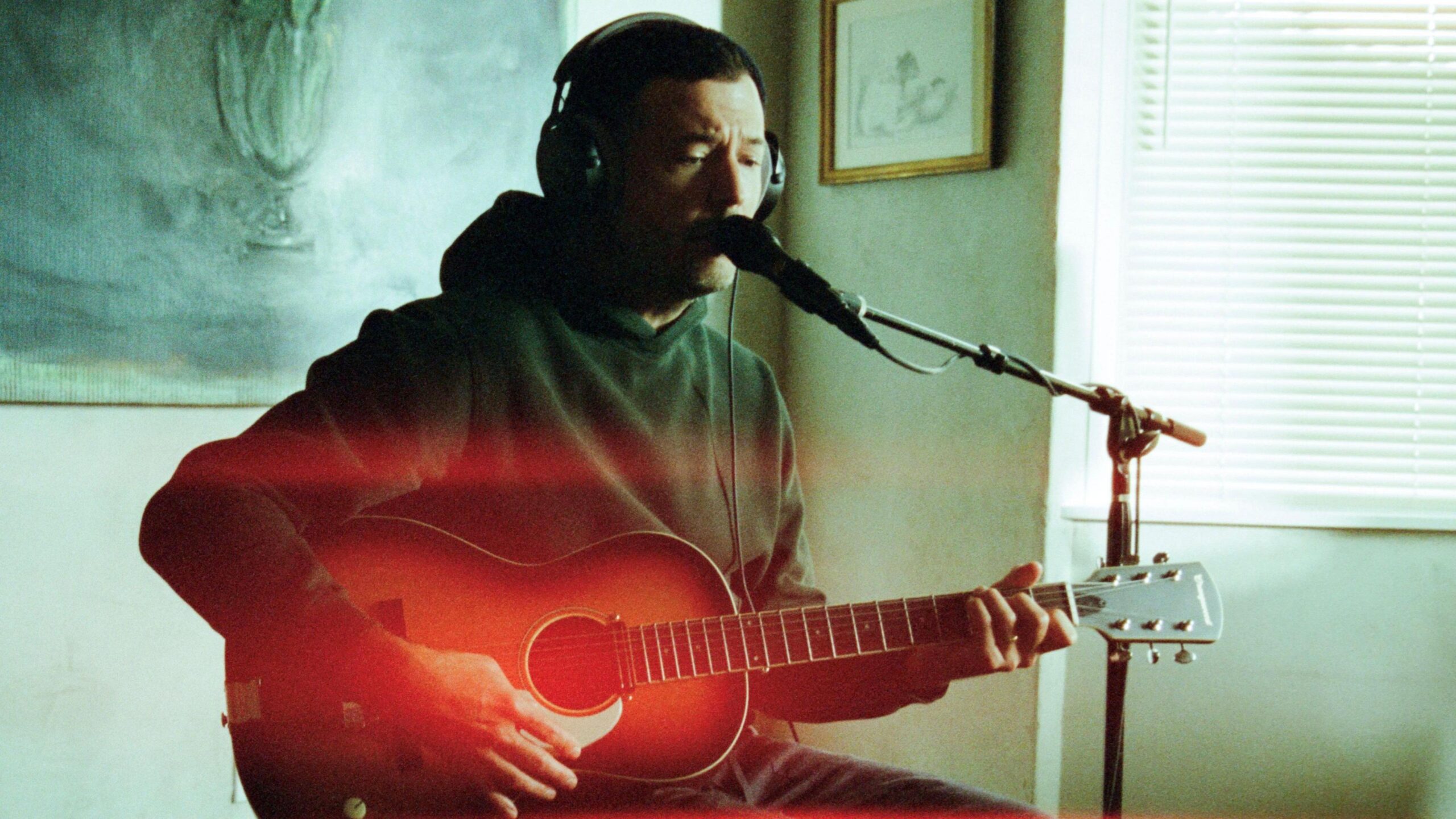

Fennell, who was previously part of indie band Barcelona, said writing his “cinematic and melancholic” music was a way to explore his feelings over being adopted.
“It’s becoming easier for me to write songs that dig deep compared to speaking about [my feelings] to even my partner or my kids,” he said.
“It is therapeutic to be able to pour it out.”
His latest album, Nobody Lives Here, continues his exploration of his identity as someone who has been adopted alongside other themes such as grief and mortality.
Fennell was born in the US and adopted at just three days old. His birth parents had not named him.
On receiving his adoption papers he learnt his parents – who were aged 17 and 18 when he was born – were second-generation Welsh immigrants.
He was also given a hand-written letter from his birth mother, which he described as “the most gutting” thing he had ever read.
“I think one of the most gutting things was the blank spaces where my name was meant to go,” he said.
“It was a really sweet note sort of explaining why it wasn’t the right time for her to be a mother and for my birth father to be a father.
“I think I’ve only read it twice, it’s so intense to read.”

From the moment he discovered his heritage Fennell embraced his Welshness.
“It was the first moment that I was like ‘I have a bit of a country of origin’,” he said.
“I sort of wrapped myself in it.
“I got like a Welsh flag to hang on my wall. I was Googling ‘Welsh people – what do they look like? What are they?’.”
He also got a Welsh tattoo that reads “echen”, meaning family or tribe.
He released his eponymous debut album in 2019.
“In choosing a Welsh name – syml – that was a bit of an honouring, at least an honouring from my perspective, and saying that this is where I come from on some level,” he said.
“And choosing a name like ‘simple’ was a bit of a reminder not to overcomplicate, whether it’s art or relationships or thinking about where you’re from and everything that comes out of that.”
He visited Wales in October 2019 to play a gig at Clwb Ifor Bach in Cardiff.
“I had this comical moment when I got out of the touring van in Wales for the first time, I had this idea that I should kiss the ground or something, like I’d returned home,” he laughed.
He said in reality he was met with a car park, but he loved playing to a Welsh audience.
“It was a sweet experience, the folks were welcoming of somebody with an imposter Welsh name,” he laughed.
Part of his performance was a Q&A session so he got to chat to the crowd.
“I remember there being a bit of a funny moment where I just couldn’t understand some of the accents,” he laughed.
He was inevitably asked about his Welsh stage name.
“I was coming into it admitting, like raising a white flag ‘I’m not Welsh so I’m not going to pretend to be’ but also explaining why it is significant to me to have a Welsh name and it was really well-received,” he said.

There are still many things Fennell does not know about his birth family and his heritage, for instance where exactly they were from in Wales.
“Back in the ’80s when I was adopted, in the US many adoptions were closed and so there was very little information,” he said.
“Even to this day if I wanted to learn more I would have to go and apply and get the approval of my birth parents to release that information and since I was 18 that’s not sat well with me.”
Also, the unknown can be scary.
The musician said all his life he has intentionally not finished TV series or books because he did not want to know the ending.
“I think I intentionally leave these big question marks,” he said.
“I save myself from knowing everything because it might not be good and so I think I guard myself in ways and I’m sure it’s rooted in [being adopted].”

Having his own children – aged 10, eight and three – has filled Fennell with gratitude for the parents who raised him as well as compassion for his birth parents.
“A big moment was when my son was born because that was the first person I’ve ever met that I’m blood-related to and that instantly filled so many voids that I knew about and didn’t know about,” he said.
It also gave him a new perspective on his own start in life.
“I have finally been able to get to a place after having three kids… where I am interested in digging in a bit more,” he said.
“The longer I wait obviously the smaller the chances I’ll get those answers.”
”When it’s your kids hitting you, you can’t leave’
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/articles/cy7gz3xdelno
”When it’s your kids hitting you, you can’t leave’

Helen Richardson
Political Reporter, NE & Cumbria
Jane Downs
BBC North East & Cumbria Investigations
- Published16 March 2025
Parents and guardians who have suffered violence at the hands of children in their care say support services are a “postcode lottery”. Despite a seeming rise in attacks, alongside greater awareness, experts agree the problem is not being properly addressed.
Here, one couple share their experience.
“She had me round the throat one day,” Angela, a guardian to a young girl, told the BBC.
“Another time she had me against the bench with a knife at at her throat, saying she was going to kill herself and make me watch.
“That was a really, really scary time that seemed to go on forever.”
After a family breakdown, Chris and Angela (not their real names) took on the care of a female relative who was still at primary school.
Over time, they say, the child’s behaviour deteriorated until the couple realised they were in physical danger.
They were open with social services from the outset, but say their concerns were “minimised” and they were just told to “keep going.”
“What do we do when she’s smashing the house up or when she’s got me locked in a room?”

“Things were escalating beyond what was safe,” recalls Chris.
“I felt pathetic, because why should I have to call the police to protect us from an 11-year-old or a 13-year old? It’s humiliating.”
Chris and Angela say they eventually had no choice but to call the police, but attending officers made it plain the child would not be taken out of the situation, nor would charges be brought.
Violence on the rise?
Experts say child-to-parent violence and abuse (sometimes known as CAPVA, CPA or APVA) can be sparked by childhood trauma or a youngster witnessing domestic abuse in the home.
It can also be more common in families with neurodiverse children.
Because there is no standard definition for this type of domestic violence, offences are recorded in different ways across the country meaning it can be difficult to measure the scale of the problem.
We asked 39 police forces in England for the number of reported crimes involving adolescent or child on parent violence and abuse in their areas in 2015, 2019 and 2023.
Of the 17 forces which responded, 10 recorded more cases in 2023 than in 2019.
In north-east England, where Chris and Angela live, North Yorkshire, Northumbria and Durham police did not provide figures, but both Cumbria Constabulary and Cleveland Police reported an increase in cases.
One former social worker – who wishes to remain anonymous – told the BBC she witnessed violence against parents first hand, sometimes from children as young as eight.
She believes that, although the subject is now more openly discussed, services offered by some local authorities have yet to catch up with the level of risk some children present.
“These parents are dealing with this on a daily basis,” she says.
“I think things like social media, trying to manage the use of mobile phones, that’s becoming a real trigger point when they’re trying to put parental controls in place, because children don’t want that and they’re acting out.
“I’ve been in households where I’ve seen significant levels of harm directed towards parents and carers from children and, even with professional intervention to try to de-escalate, it has resulted in police call outs.”
Chris and Angela felt social services encouraged them to offer their child “leeway” rather than making it clear her behaviour was unacceptable.
“We’d tell them ‘look, we don’t think we can go on with this’,” says Chris. “We don’t think this is good for us or her.
“They would just blow smoke up (our backsides) about what a good job we’re doing. We felt hopeless.”
Angla adds: “Now she just thinks this is what people do.
“When you’re in an abusive relationship, you have the option to go. But when it’s your kids you don’t, do you?”

CAPVA researcher Dr Nikki Rutter believes early intervention is key for carers like Chris and Angela.
“Local authorities here in the North East are very good at responding to families where there are very particular high risk needs,” she says.
Dr Rutter points to what she sees as exemplary areas of practice in certain areas of the country, including Wales and Norfolk, but says problems lie in the systems that should refer families for help when they first have issues.
“Early intervention is very, very rarely occurring in any of the local authorities throughout the North.
“They’re dealing with the problem rather than preventing it in the first place.
“Sometimes it can be services saying ‘this isn’t our responsibility’, ‘we’re not commissioned to do this’ or ‘we are restricted in terms of staffing’.
“For those families it must just feel like there’s no way out or there’s not many people listening.
“Families are crying out for help, quite often from the child being four to five years old, and nothing is being done.”
Government plans pending
The government has pledged to halve violence against women and girls in the next ten years.
It says tackling abuse of parents in their own homes is a “vital” part of that challenge.
A Home Office spokesperson said: “We are continuing to develop our specific approach to child-to-parent abuse, taking on board the contributions to last year’s consultation.
“We will set out our plans in this area and respond formally to the consultation in the coming months.”

In County Durham, the police and county council have started jointly funding “ambassadors” to run a “Respect” programme with families that need help.
Young people and parents have their own workers who then come together over time to make changes.
Jackie Staff, one of the support workers, says violence towards parents and guardians is only just really starting to be discussed more openly, but things are changing as a result.
“We’re getting some real successes from the families,” Ms Staff says.
“They’re telling us that it is working and the behaviour has reduced.”
But Joy Allen, Durham’s Police and Crime Commissioner, says a lot of parents are still suffering in silence.
“One in 10 women who’ve been murdered by a man have been murdered by their son,” she says.
“That’s a significant fact that we need to address and early intervention is much better than escalating.
“We want people to have the confidence to come to us for support. It isn’t anything to be ashamed of and there is help out there.”
‘Let’s stop pretending’
Angela and Chris are clear about what they think needs to change.
“Definitely funding for children’s mental health I think is a massive thing, but also child-to-adult violence is not talked about,” says Angela.
“Parents are embarrassed. We were embarrassed.
“We didn’t want to tell anyone that this child has been violent. I think that’s a massive issue.”
Chris says he feels seeking support somewhere you can be honest about exactly what is happening is essential.
“Even if it’s Facebook groups, it’s people going through the same thing,” he says.
“Let’s stop pretending that this is not happening, that children aren’t being physically violent towards the parents.
“It takes the adults to do that, because the kids are never going to admit it.”
‘We love our adopted children… but after years of violent attacks we had no choice but to put them back in care’: Shattered parents reveal why so many adoptions fail to HELEN CARROLL
‘We love our adopted children… but after years of violent attacks we had no choice but to put them back in care’: Shattered parents reveal why so many adoptions fail to HELEN CARROLL
By HELEN CARROLL FOR THE DAILY MAIL
Published: 01:58, 29 November 2024 | Updated: 16:13, 29 November 2024
Having met while working at a children’s charity, Naomi and Martin were aware of the challenges of adopting children who have had a difficult start in life.
They also believed that, given their experience, if any couple had the skills needed to provide the right mix of love, nurturing and guidance required, it was them. However, 12 years after adopting two young children – years in which the parents were beaten and abused so violently they regularly had to call the police, and both suffered nervous breakdowns – the children, now aged 15 and 16, are back in care.
They lay the blame for this heartbreaking situation squarely on their local authority which, they say – due to a lack of funding and a ‘pass the buck’ culture – totally abandoned them to their fate.
Says Naomi, 45: ‘We did our best, but the children desperately needed professional help which, once they were officially adopted by us, was almost impossible to access.
‘I’m not saying that I thought we’d ‘save’ them, but I, naively, believed that with love, stability and permanence we were providing an environment in which any difficulties that arose could be worked through.
‘We never bargained for being kicked, hit, spat at and verbally abused – Martin is deaf in one ear after one particularly vicious punch from our son – and certainly not for the relationship with our children to completely break down.’
It’s notable, and poignantly sad, that this couple still refer to the brother and sister, whom they welcomed into their home aged two and three, as ‘theirs’. They love them and feel guilty about what happened.
They’d gone into the adoption process longing for a forever happy family, after learning they were unable to have children themselves.

Adoptive parents have been left traumatised, their marriages wrecked – and even driven to taking their own lives – by a system incapable of supporting them, writes Helen Carroll
It’s a tragedy shared by hundreds of adoptive parents across the UK, who’ve been left traumatised, their marriages wrecked – and even, in extreme cases, driven to taking their own lives – by a system woefully incapable of supporting them.
One support group, PATCH (Passionate Adopters Targeting Change with Hope), which has 700 members, is campaigning for systemic change to address this ‘crisis’. Most members share the same grievance: that children are almost always removed from their birth parents due to significant abuse or neglect, which often begins during pregnancy, where they are exposed to drugs and alcohol. This leaves the children with symptoms of extreme trauma.
However, when behavioural issues manifest post-adoption – some of which can be genetic – the adoptive parents are left to fend alone and, ultimately, blamed when the situation becomes unmanageable.
According to figures from Adoption UK, 65 per cent of adoptive parents experience violence or aggression at the hands of their children. And, based on responses to the charity’s annual survey, the number of adopted children leaving the family home ‘prematurely’ is rising, from three per cent in 2021, to seven per cent in 2023.
‘There’s a common, but false, belief that trauma is healed through love, and therefore adoption is the happy ever after, which any psychologist or psychotherapist will attest, it is not,’ says Fiona Wells, who runs PATCH and is herself a social worker, working in fostering, and also both an adopter and adoptee.

According to figures from Adoption UK, 65 per cent of adoptive parents experience violence or aggression at the hands of their children
‘Social workers are not experts in trauma, they’re experts in risk and family life. What these families need is trauma-informed therapeutic, as well as practical, support, but once an adoption is finalised the children, and any issues they have, seem to be considered the responsibility of the adoptive parents.
‘Support is, technically, available, through regional adoption agencies, but there are often lengthy delays and misdirected guidance towards inappropriate solutions which perpetuate the problems.’ Naomi and Martin’s experience was sadly typical. The children, Tamsin and Joseph, had been taken into foster care aged one and two having suffered extreme neglect. Their mother abused drugs and alcohol, and they were not fed or washed. Their biological father was in prison for domestic violence.
Joseph was still a toddler when he started lashing out at them. Naturally, the couple turned to their social worker for guidance.
The only advice was to use ‘non-violent restraint’, such as changing the subject and distracting the child in a confrontational situation, and ‘natural consequences’ tactics i.e. leaving it to the child to work out the results of their actions themselves.
Blunt instruments indeed when you are being punched in the head or attacked with a baseball bat.
As one specialist adoption solicitor put it, with highly damaged children the approaches are like ‘applying an Elastoplast to an arterial wound’.
Unsurprisingly, things got worse. Their daughter’s violent outbursts began after she started secondary school.
Naomi believes this was due to her being dyslexic and on the autism spectrum – although she was never diagnosed. Again, the social workers were of little use.
Tamsin was 14 when, after a fall out over something Naomi struggles to recall, she attacked Martin so viciously, biting him and hitting him with a bat, that Naomi had no alternative but to call the police for help.
‘They arrested her, keeping her in a cell overnight, which was horrific, but they thought it would teach her a lesson,’ says Naomi. ‘Sadly, it didn’t, and it happened again, two weeks later.’
Then, one day she returned from a brief dog walk to find Joseph and Tamsin brutally attacking one another, close to the top of the staircase, ‘biting, scratching, kicking, hair pulling and spraying deodorant into each other’s faces’.
After trying, in vain, to separate them, in desperation Naomi called the police again. By the time officers arrived, the siblings had fled and Joseph was later found, sitting on a railway bridge, threatening to jump.

When behavioural issues manifest post-adoption – some of which can be genetic – parents are left to fend alone and blamed when the situation becomes unmanageable (file image)
Police managed to pull him to safety, and he was referred to CAMHS (Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services). The couple were told Joseph needed ‘dyadic developmental psychotherapy’, a specialist treatment for children who have been hurt or neglected in their early years, which would require both Naomi and Martin to attend weekly sessions.
This proved very difficult for Martin. As the family breadwinner, who now works in finance, he was unable to take time off work in the middle of the day. Though evening sessions were available, the couple’s request for these was ignored. Social workers were unsympathetic, and highly critical of him in reports.
Both children developed serious mental health problems, and would regularly self-harm, shutting themselves in the bathroom. At their wits’ end, the couple took the lock off the bathroom door – only to be told by social workers to replace it to ‘protect the children’s privacy’.
‘I was terrified one of them might die and begged social workers to get them urgent appointments with CAMHS, which still felt like our only hope, yet there seemed to be no urgency back then – though I understand they’ve had referrals now, after the adoption has broken down,’ recalls Naomi.
Everything came to a head at the beginning of the year when Tamsin had gone missing. Martin was out with Joseph in the car, scouring the streets, when he had what can only be described as a nervous breakdown. He later described how he’d started driving very quickly, feeling like he wanted to die.
‘Martin was full of remorse,’ says Naomi. ‘But we realised we were both so broken we could no longer cope and asked that the children be taken back into care.’
Initially the siblings were taken into care under a Section 20 order, a voluntary agreement between the adoptive parents and the local authority for them to provide temporary care, but now have a ‘full care order’, which means they will remain in local authority homes until they are 18.
The couple still see the children – last week Naomi met Tamsin to go shopping and took Joseph for tea and cake. On another occasion, Martin took Joseph to play pool. The last time the children visited the family home, for Sunday lunch, they stole £100 from a safe. ‘We miss them and still consider them our children,’ says Naomi.
‘And we don’t put any of the blame for what’s happened on them. They’ve developed a fight or flight response as a result of their early trauma and haven’t had the professional support they need. However, as much as we still love them both, it’s a relief they don’t live with us any more.’
One explanation for the rise in cases of children having to leave their adoptive home is the effects of widespread cuts in funding to local authorities and CAMHS, says Alison Woodhead, of Adoption UK. ‘Adopters often feel quite abandoned, not knowing what they’re entitled to or what support is out there.’
This was certainly the case for Stephan, a little boy who, together with his older sister Juliet, was adopted by Sophie Greenwood and her wife, Susie, a schoolteacher, in 2012, when they were aged two and three.
Both children were malnourished, covered in sores and fleas and so terrified of water that Sophie and Susie were unable to bath them, unless they climbed in too.
While Juliet developed normally, Stephan had abnormal brain development that could have been caused by exposure to toxins in the womb, as well as suspected foetal alcohol syndrome. He was diagnosed with autism, ADHD and oppositional defiant disorder (ODD).
‘We wanted them to stay together, so we could all be a forever family,’ says Sophie. ‘However, we had no idea what a fight we had on our hands to get our son the support he needed.’ As a toddler, he was easy to pick up and distract, but as he grew bigger he grew increasingly violent – biting and kicking his parents and his sister.
Warned not to physically restrain him, Susie and Sophie would hold a kickboxing pad in front of them to soften the blows.
Eventually, when he was eight, they couldn’t cope any more.
‘A therapist, assigned by the local authority, agreed that our son needed a specialist residential school, but said the only way we’d secure one was to report any significant physically aggressive incidents to the council and the police, so there was a log.
‘We did this, and the local authority pushed back, placing both children on the child protection register under suspicion of ’emotional abuse’.’
Stephan moved to the residential school aged ten, leaving Juliet at home. In theory, this meant Susie was able to return to work as a teacher. However, she was now on record as being the mother of children ‘at risk’.
‘The fight for support and the shame just broke her,’ says Sophie. ‘She was so tired and constantly ruminating over the injustice of it all.’
One evening, in late 2022, Susie took her own life.
Sophie sobs as she recalls breaking the terrible news to their children — Susie’s death heaping further trauma on top of what they had already endured.
Juliet, 15, is developing normally, while Stephan still comes home regularly – but remains prone to lashing out. Although she cannot bear to imagine her life without her two children, Sophie admits that, had she and Susie known what lay ahead, they would have been unlikely to proceed with adoption.
Adoption specialist solicitor Nigel Priestley says the legal firm where he is a senior partner, Ridley & Hall in Yorkshire, is contacted by about 150 adoptive families in crisis a year.
‘Long gone are the days when most babies adopted came from teenagers, in mother and baby homes,’ says Nigel. ‘We have a whole host of children coming through who carry significant issues with them. Specialist support for these children costs local authorities a fortune and, over the last ten years, the services that provide support have been cut to the bone.’
Alison from Adoption UK stresses that this lack of funding is the issue, and that the devastating impact of adoption breakdown on the child should not be forgotten. ‘When adopted children and young people leave the adoptive family home prematurely it is devastating for all concerned, particularly the young person.
‘It’s almost always because they are let down – by adoption services, by mental health services and by the education system. Most adoptive families describe a constant battle to get the support their children and young people need. When children and young people do leave their adoptive family home prematurely, many return there. And many adopters with children and young people living away from home are still intimately involved in their lives and their care.’
As one mother, whose marriage didn’t survive after she and her husband adopted three traumatised, and later violent, siblings who had suffered terrible neglect and abuse, says: ‘I don’t blame the boys for how they behave – if I’d had their start in life, I’d no doubt struggle to control my emotions too. I blame the system for not giving them the help they needed. There should have been ongoing support in place from the get-go.’
Hundreds of devastated parents up and down the country, whose adoptions have been similarly disrupted, agree wholeheartedly.
- For support, visit the PATCH website at ourpatch.org.uk
- Names of children and parents have been changed.
Uncertainty for families as China ends foreign adoptions
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/articles/crmwrpe3m3do
Uncertainty for families as China ends foreign adoptions

Nathan Williams
BBC News
- Published6 September 2024
China has announced that it is ending the practice of allowing children to be adopted overseas, bringing uncertainty to families currently going through the process.
A spokeswoman said that the rule change was in line with the spirit of international agreements.
At least 150,000 Chinese children have been adopted abroad in the last three decades.
More than 82,000 have gone to the US, a greater number than anywhere else in the world.
At a daily briefing Thursday, foreign ministry spokeswoman Mao Ning said in the future Beijing would only allow foreign nationals who are relatives to adopt Chinese children.
She did not explain the reason for the decision, other than saying it was in line with international agreements.
Ms Mao thanked families “for their desire and love in adopting children from China”.
The ban on foreign adoptions has created uncertainty for hundreds of families in the US currently going through the process of adopting children from China.
In a call with US diplomats in China, Beijing said it would “not continue to process cases at any stage” other than those cases covered by an exception clause. This position was confirmed by spokeswoman Ms Mao.
Washington is seeking clarification from China’s civic ministry.
China’s controversial one-child policy, introduced in 1979 when the country was worried about a surging population, forced many families to abandon their children.
Families that violated the rules were fined and, in some cases, lost jobs. In a culture that historically favours boys over girls, it often meant that female babies were given up.
International adoption was formalised in the 1990s, and since then tens of thousands of children have been adopted, with about half going to parents in the US – including celebrities like Meg Ryan and Woody Allen.
However, the international adoption programme has at various times come under criticism. In 2013, Chinese police rescued 92 abducted children and arrested suspected members of a trafficking network.
Critics at the time pointed to China’s one-child policy and adoption laws, which they said had created a thriving underground market for buying children.
A number of countries have expressed concerns about international adoptions.
Denmark has closed its only overseas adoption agency, over concerns about fabricated documents. The Netherlands has also said it will no longer allow its citizens to adopt children from abroad.
But Beijing has also altered the way it views children. In stark contrast to the position taken by officials at end of the 1970s, the country’s leaders now worry there are not enough babies being born to sustain the population.
In 2016 China scrapped the one-child policy and in 2021 Beijing formally revised its laws to allow married couples to have up to three children.
In recent years, the Chinese government also offered tax breaks and better maternal healthcare, among other incentives, in an attempt to reverse, or at least slow, the falling birth rate.
But these polices have not lead to a sustained increase in births, and in 2023 the country’s total population fell for the first time in 60 years.
Adopted children to have closer contact with birth families
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/articles/c3vl5w3zy2eo
Adopted children to have closer contact with birth families

Sanchia Berg and Katie Inman
BBC News
- Published 7 November 2024
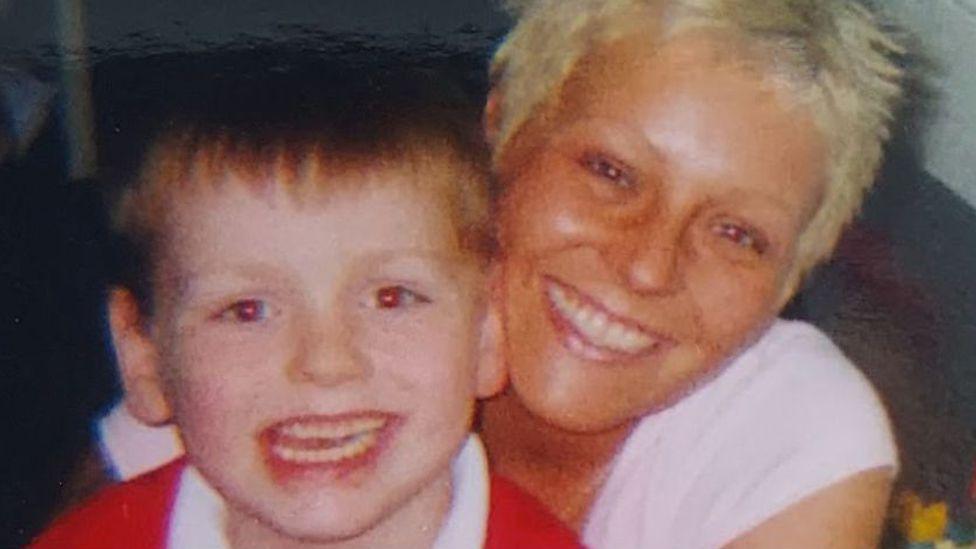
Adopted children are likely to be allowed much closer contact with their birth families in the future as part of “seismic” changes recommended in a report published today. Some families say the changes are long overdue but others worry they may deter people from adopting. Angela Frazer-Wicks’ two sons were removed from her care and adopted in 2004, when they were aged five and one. She was in an abusive relationship and had problems with addiction and her mental health. By 2011 Angela had recovered, she was in a new relationship, and had a baby daughter. The local authority was not involved in her daughter’s care. Angela’s sons and their adoptive parents had stayed in touch with her writing letters and sending photos once or twice a year. But when the older of the two boys became a teenager, he told his adoptive mother he no longer wanted to write to his birth mother. Angela carried on sending cards, but heard nothing back for years. Then out of the blue, in 2020, Angela received an email from her eldest son. It turned out he had been trying to contact her, but the local authority had told him that wasn’t possible. Last month, Angela met her eldest son in person – it was the first time she had seen him for 20 years. “It was amazing for me,” Angela says, “even more so for my daughter – she’s waited her entire life to meet her brother.”

Adoption is the state’s most powerful intervention in family life. It is a permanent break between a child and their birth family, and alters the child’s identity forever. In law they are no longer the child of their birth parents, and most adopted children grow up without seeing or knowing any of their birth family. Around 3,000 children are adopted in England each year. It’s a process that must be authorised by judges in family courts, who set out the level of contact the child will have with their birth parents usually just letters, sent twice a year, via an intermediary. While adoption law has evolved over the years allowing children to know more about their history than they once did, in some ways, families say, adoption is still very much stuck in the past. Now a new report from a group set up by the most senior judge in the family court, external says wholesale reform of the system is needed. “Letterbox” contact between adopted children and birth families is outdated, the report says, instead recommending face-to-face contact where that is safe. The extremely detailed report is strongly supported by Sir Andrew McFarlane who says there is no need to change the law for this to happen. The report is likely to influence family court adoption hearings throughout England and Wales. Angela Frazer-Wicks describes her experience of adoption as a “life sentence without any right to appeal”.
As chair of trustees of the charity Family Rights Group, she is pleased mothers like her will have more chance to continue seeing their children after they have been adopted. “It’s a seismic shift,” Angela says. “It’s been such a long time coming. My hope is that we start to see just a bit more compassion towards birth families – they are so often seen as the problem.”
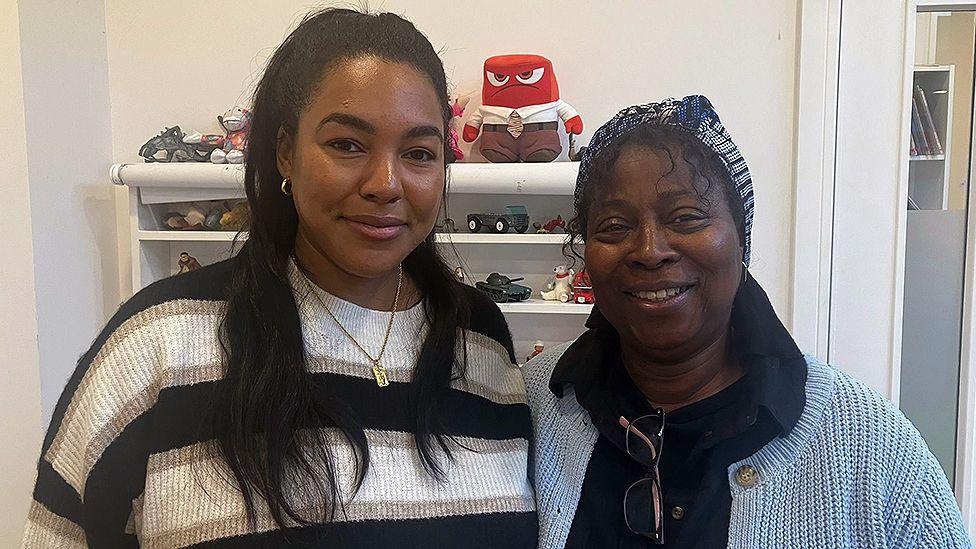

While meeting birth family can be very positive for some adopted children, face-to-face meetings aren’t good for all children in this position. When Cassie was adopted aged three, she constantly worried about the mother she’d been take away from. Out shopping with her adoptive parents Dee and John, Cassie would even ask if she could buy groceries for her birth mum. Dee was advised it would be reassuring for Cassie to meet her birth mother face-to-face. Their reunion, in a noisy contact centre, went well but the following day Cassie was very tired, pale and limp. Dee decided to take Cassie to the doctor, and by the time they arrived at the surgery Cassie was trembling and vomiting uncontrollably. But there was nothing physically wrong the doctor said Cassie was in shock. For nearly two years Cassie and Dee went to specialist therapy. Cassie still seemed to worry about her birth mother, and would try to call her on a toy telephone. Another meeting was arranged, in a quieter environment, with support. After that, Cassie, who is now aged 30, says she didn’t want to see her birth mother again. “I never felt a strong urge,” she says. “I had all the information about her.”
More reporting from family courts
With more recent adoptions, there is a new kind of risk. Children can trace their birth family online and some will go and meet them. That can lead to conflict with adoptive parents, even adoption breakdown. “The children become very emotionally mixed up,” says Sir Andrew McFarlane, the head of the Family Court in England and Wales.
“If you’re trying to work out who you are you in the world, and you have some memory of the family you lived with until you were four or five it’s almost natural to try and trace them and be in touch with them.”
Without expert help, this can have disastrous consequences. In 2021 one couple told the BBC it was “devastating” to see their two adopted sons turn against them and get drawn into crime, after they had been reunited with their birth family. There is no accurate data on how many adoptions break down. The charity Adoption UK has said it varies between 3% and 9%. Following a four-year review and consultation, the 170-page report published today says greater consideration should be given to whether adopted children “should have face-to-face contact with those who were significant to them before they were adopted”.
The report is intended as a review of the adoption process and a “catalyst for positive changes”.
Among the dozens of other recommendations are reforming the law on international adoption, and setting up a national register for court adoption records to make it easier for people to find their own files. The report also recommends dropping the term “celebration” for parents’ last visit to court with the child they are adopting. Many adoptive parents agree the current “letterbox” system of contact is not effective. In a 2022 survey, Adoption UK found that most prospective adopters believed that standardising direct contact would deter people from adopting, at a time when the number of people coming forward to adopt is in decline. But at the same time, it found that 70% of those looking to adopt believed that direct contact should be standard practice, if considered safe. Others think it could create further problems. Nigel Priestley is a specialist adoption solicitor and an adopter himself. He has seen the issues this contact can cause. “I think it’s enormously risky,” he says. “In my view there is a grave danger that if you once open Pandora’s Box shutting it will be impossible.”
A Department for Education spokesperson said the value of children growing up in a loving family “cannot be underestimated”. And for many children in care, “adoption makes this happen”.
“We know that adoption has a profound impact on everyone involved, and it’s vital that the child’s best interests are protected and remain at the heart of the process.”
Clarification 8 November 2024: This story has been amended following updated information supplied by Adoption UK
‘They just took the baby away’: Family speaks out in church-run homes scandal
‘They just took the baby away’: Family speaks out in church-run homes scandal
- Wednesday 16 October 2024 at 10:27pm


A family has come forward following an ITV News investigation into cruelty and abuse at ex church run mother and baby homes, Social Affairs Correspondent Sarah Corker reports
Further allegations of abuse and neglect at a former church-run mother and baby home in Cumbria have emerged, following an ITV News investigation. Earlier this year we revealed that 45 babies who had died at St Monica’s home – in Kendal were buried in an unmarked grave in the town’s cemetery.
St Monica’s was one of hundreds of homes for unmarried mothers across England.
Between 1949 and the mid-1970s, an estimated 200,000 women were sent away to homes run by churches and the state where they were pressured and coerced in to give up their babies for adoption. Other infants died through poor care.
Since our first report aired in July, the family of one of those children has come forward and told ITV News that their mother was lied to about the fate of her baby daughter, Faith, and was never told where she was buried.
Norah Everard was in her 80s, and dying from cancer, when she told her family for the first time about the trauma she’d endured decades earlier as a teenager in 1941.
Pregnant and unmarried, she was sent away to St Monica’s, which was run by the Diocese of Carlisle, to have her baby.
Norah’s son Bob Chubb recounted the details that his late mother shared with him and his wife Carole about the “cruel” home.

“We were all round the table one Christmas, and she said ‘I’ve got something important to tell you both. Bob you weren’t my first born’, and then she told me about being raped as a young school girl, going to St Monica’s in Kendal to have the baby, and the baby was stillborn, called Faith,” Bob told ITV News.
Burial records seen by ITV News suggest that Norah was lied to, they show that Faith wasn’t stillborn and that she had lived for 12 hours and was later buried in an unmarked grave at Parkside Cemetery in Kendal – one of the 45 babies who were buried in secrecy.
If you’d like to share your story please get in touch with Sarah on the following email: Investigations@itv.com
“I don’t think she was told the truth. I think some terrible things went on,” Mr Chubb said. Carole Chubb, Bob’s wife, said: “It really really disgusts me. They just took the baby away and said the baby’s dead and that’s it. Did they even given her any milk? Would she have survived? “Norah told me it was cruel place, they made the women scrub floors when they were heavily pregnant and they were refused pain relief in labour as a punishment.”
Bob and Carole share their family’s story and concerns about how babies were treated
Concerns have been raised by other families about the poor care of sick and premature babies at the home in the decades after the war, while official documents from the archives paint a disturbing picture of neglect, cruelty and suffering inside St Monica’s. Bob revealed that he too was born prematurely at the same home in the late 1940s, and feels ‘lucky’ that he survived.
The acting Bishop of Carlisle Rt Rev Rob Saner-Haigh described what had happened to Norah and her daughter as ‘wrong’ and said he was ‘really sorry’ for the way women and children had been treated.
The acting Bishop of Carlisle Rt Rev Rob Saner-Haigh answers questions from ITV News
Since allegations of abuse first emerged, 20 people with a connection to St Monica’s have contacted the Diocese requesting access to their family records. “The Church of England should do all it can to support people who have lived with the trauma. We need to listen and give them a choice in decision making so they can tell us what they need and as an organisation we show them the love and dignity that they weren’t shown before,” he said.
The family of another baby, Stephen Holt, who died aged 3 months old at the home in 1964, are now campaigning for a permanent memorial to the 45 babies.
It was years later when baby Stephen’s mother Judith Hindley first told her husband, also called Stephen, of the abuse she endured at the ‘draconian’ home in the late 1960s. “Judith was 17 at the time and told me how she was forced to clean floors and kitchens while heavily pregnant. They were being punished,” he said. “Her son Stephen was born with disabilities and needed to go to hospital, but he was cruelly denied proper medical care and died 11 weeks later.” She never recovered from that trauma and in 2006, Judith took her own life close to the cemetery where her baby is buried.
Stephen Hindley explains what happened to his wife Judith at St Monica’s and why he is campaigning for a memorial
Cumbria Police has confirmed it is still investigating allegations of historic abuse at St Monica’s and said it “would welcome any new information which would assist officers…following concerns raised in relation to these premises”. Westmorland and Furness District Council which owns the cemetery where the graves are located said: “We are currently exploring options and reaching out to others who may wish to be involved or consulted on the possibility of marking the unmarked graves at Parkside Road cemetery, Kendal relating to the former St Monica’s Maternity home.”
Department for Education spokesperson said: “We have the deepest sympathy with all of those who are affected, the practice was abhorrent and should never have taken place.
“While we will not be able to quickly make every change we would like, we will look at whether there is any more we could do to support those affected.”